Wound healing after surgery is the most important physiological process, the success of which determines the rate of recovery of the patient and his future health. After all, sometimes even after a successful surgical intervention during the rehabilitation period, complications arise that are associated precisely with the imperfection of wound care.
How does a wound heal after surgery?
The first and most important thing that the surgeon does to speed up the healing of the wound after the operation is to bring its edges together with the help of suture material. In other words, stitches. Thanks to natural regeneration processes, over time, the wound grows together and becomes covered with new tissues.
If you delve into biology, you can distinguish three sequential healing processes.
The first is epithelization. The resulting squamous epithelial cells cover the most affected areas (with the deepest tissue damage).
The second process is convergence or contraction of the wound, when the edges are connected to each other, completely hiding the exposed mucosa. And then the third, final mechanism of postoperative wound healing occurs - this is collagenization, when collagen fibers cover the delicate skin of the wound, providing it with strong protection.
Important! If a person is healthy, then everything happens quickly and efficiently. A weakened or diseased organism sometimes does not have enough biological capabilities for this, therefore, it is necessary to select special auxiliary preparations for wound healing and take care of it more carefully.
Preparations for wound healing after surgery
From a person's first aid kit, it can sometimes be determined that he has recently undergone surgery. Because in this case, not only patches and bandages appear at his home, but also all kinds of solutions, gels and ointments for healing. Some were advised by a doctor, others were recommended by a neighbor or colleague, others were bought as a result of advice from Internet forums. And often half of the acquired is wasted, because the choice of the drug largely depends on the type of wound and the stage of its treatment.
External preparations
A good outdoor product should have the following properties: 
- disinfectant (does not allow the formation of harmful microbes and destroys old ones);
- anti-inflammatory (stops and prevents inflammatory processes);
- anesthetic (relieves pain);
- regenerating (promotes speedy healing).
But it is not necessary to buy 4 different drugs in order to quickly heal the wound. Modern tools usually have two, three or even all four properties, which makes their use convenient. So, how to speed up wound healing after surgery.
Primary processing
Care of the wound and the skin around the wound should be regular. The frequency of making dressings or simply applying an external agent not under a bandage is determined by the attending physician. But before using the gel or ointment, the wound must be treated with an antiseptic, which will cleanse it of dirt and particles of dead skin, preparing the tissues for the main healing agent.
Of these antiseptics, you can use the "good old" penny remedies: hydrogen peroxide, potassium permanganate solution, furacilin, chlorhexidine. Depending on the specifics of the wound and its location, the doctor will recommend which drug is best suited.
The main tool for rapid wound healing
It can be an ointment or a gel. They differ not only in their consistency, but also in their purpose. The ointment is applied to dry wounds that tighten and tear, and therefore do not heal. And the gel is better suited for weeping wounds, because it does not form a film and allows the skin to breathe.
Salicylic ointment
An ointment with antibacterial properties known since Soviet times. It is applied under a sterile bandage after pre-treatment of the wound with peroxide. You can buy salicylic ointment for only 20-30 rubles (25 g).
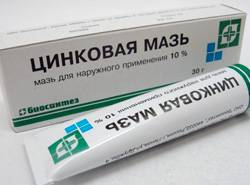
Despite the fact that this is an ointment, it dries up weeping wounds well and heals them. Contains zinc - a useful mineral that promotes cell division and skin regeneration.
Previously, zinc ointment was produced in dark glass jars. Today you can buy it in tubes, for 30-40 rubles per 30 g.
Levomekol
A popular antibiotic ointment that can draw pus and other dirt out of the wound. It also has regenerating properties. Must have in the surgical department of any hospital. It is relatively inexpensive: 120-130 rubles for 40 g.
eplan
It is also a fairly well-known external wound healing agent used in pregnant women and children. It has bactericidal, regenerating and anesthetic properties. It costs 100-110 rubles for 30 g.
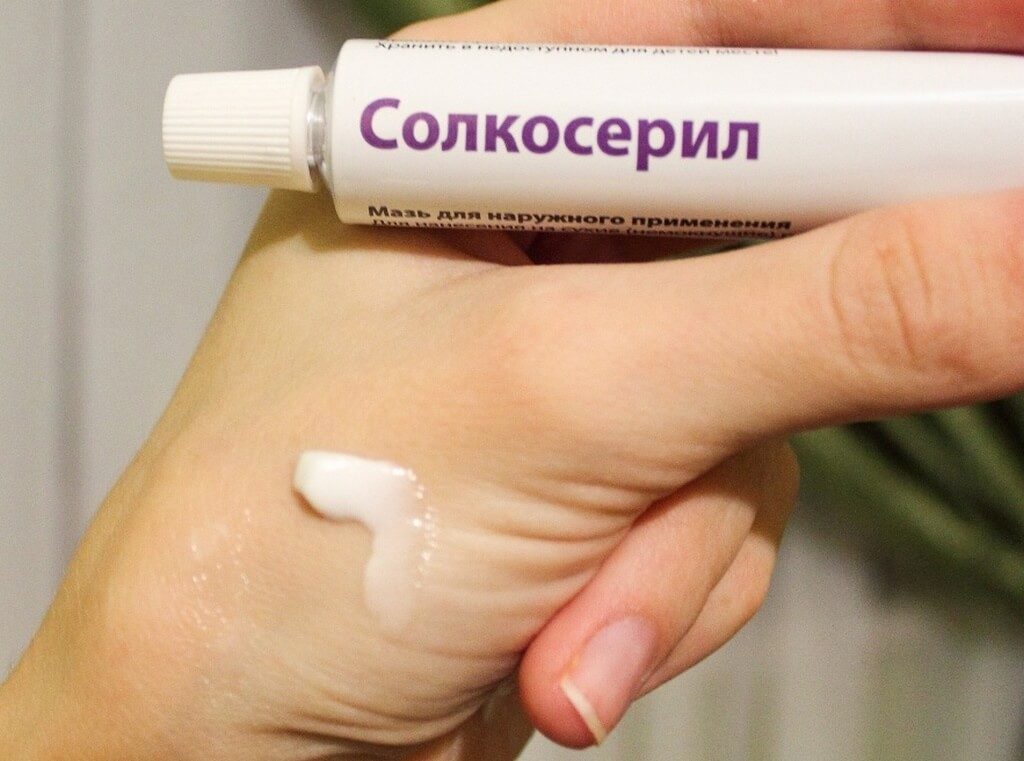
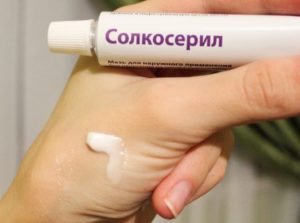
A modern remedy based on calf's blood extract. It heals well and is usually used in cases where cheap drugs do not help. Available in the form of ointment and gel. The approximate cost of a 20-gram tube is 280-300 rubles.
Argosulfan
Or its analogue - Sulfargin. This is an ointment with silver extract, which perfectly disinfects the wound in addition to its healing and regenerating properties. Especially good for purulent postoperative wounds. For 40 g you will have to pay 350-370 rubles.
In addition to gels and ointments, another type of external preparations is actively used today - powders (powders). They are ideal for weeping postoperative wounds, because they have not only healing, but also absorbent properties - they absorb excess moisture. This, for example, Ambulance, Baneocin. Of the powder preparations of the Soviet era, many remember Streptocide. You can buy tablets and crush them, or immediately purchase a package of powder for 30-40 rubles for 2 g.
Oral preparations
The human body is a whole. And in order for the postoperative wound to heal faster, it is not enough just to smear it with a good remedy. You also need to help yourself from the inside, strengthening the immune system and creating all the conditions for quick healing. Vitamin-mineral complexes will help with this, in which the percentage of vitamins A and C, as well as zinc and omega-3 fatty acids, should be increased.
Nutrition for rapid wound healing after surgery
Instead of vitamin and mineral complexes (or at the same time with them), you can just eat right. A balanced diet also has a positive effect on recovery after surgery, in general, and on wound healing, in particular. And it also implies the presence of the previously listed components in the products. We concretize.
If the products listed above contribute to the speedy regeneration of the skin, then seasonings can be added to dishes to disinfect it from the inside. Turmeric, ginger, cloves, and even regular black or red pepper have antibacterial properties and help speed up wound healing.
Wound care rules
In order for the wound to heal faster, complete sterility must be observed. Even the simplest abrasion requires compliance with this condition, not to mention a complex open postoperative wound. Therefore, the hands of the person who will carry out the treatment should be washed with soap or wiped with alcohol. In the room where fresh wounds are treated, everything should also be sterile. Therefore, dressings in hospitals are done in dressing rooms, in which quartzization is periodically carried out. At home, you can use a portable quartz lamp.
Treatment of a postoperative wound begins with its cleansing. Peroxide, a pink solution of potassium permanganate or chlorhexidine should be poured over the wound or wiped with a sterile bandage soaked in one of the products.
Attention! When treating postoperative wounds, it is not recommended to use cotton pads and sticks. First, they are non-sterile. Secondly, the villi can remain inside the wound and provoke suppuration.
After treatment, the wound should dry out a little. If necessary, you can speed up the process with a sterile bandage. Then you can take an ointment or gel and apply the product according to the instructions, with or without a bandage.
At the next dressing, remove the old bandage carefully so as not to damage the tissue. If the bandage is dry, it must be soaked by watering with chlorhexidine, for example. Plain water is not recommended.